Corrugated shipper boxes are packaging containers made from corrugated cardboard, typically consisting of three layers — a wavy inner layer (corrugated medium) sandwiched between two flat outer layers (liners). These boxes are designed for transporting and protecting goods during shipment. Known for their strength, durability, and versatility, corrugated shipper boxes are widely used in various industries for packaging and logistics purposes. They come in different shapes and sizes, offering a customizable solution for different products and shipping requirements. The corrugated structure provides added strength and rigidity, making them suitable for safeguarding products from damage during transit. Additionally, corrugated shipper boxes are often chosen for their eco-friendly characteristics, as they are recyclable and contribute to sustainable packaging.
Table of Contents
Materials Used
Corrugated shipper boxes are typically made from specific materials that contribute to their strength, durability, and versatility. Here are the key materials used in the manufacturing of corrugated boxes:
- Corrugated Cardboard:
The primary material used for corrugated boxes is corrugated cardboard. It consists of three layers:
- Corrugated Medium: This is the wavy inner layer that provides strength and rigidity to the box. It is made from a fluted sheet of paper.
- Liners: These are the flat outer layers that sandwich the corrugated medium. They are made from layers of paperboard. The liner on the outside is known as the “face” or “liner,” while the one on the inside is called the “backline.”
- Paperboard: The liners of corrugated boxes are often made from paperboard. Paperboard is a thick, paper-based material that provides a smooth surface for printing and contributes to the box’s overall structural integrity.
- Adhesives:
- Adhesives are used to bond the layers of corrugated cardboard together. The choice of adhesive is crucial for maintaining the box’s strength and stability. Water-based adhesives are commonly used for bonding the layers.
- Inks:
- Inks are used for printing information, branding, and labels on the corrugated boxes. Soy-based or water-based inks are often preferred for their environmental friendliness.
- Coatings and Treatments: To enhance the box’s performance, coatings and treatments may be applied. For example:
- Water-resistant coatings: Protect the box from moisture during transportation or storage.
- Anti-static treatments: Reduce the buildup of static electricity, which can be important for packaging electronic components.
- Recycled Materials:
- Many corrugated boxes incorporate recycled materials, contributing to sustainability efforts. These recycled materials can come from post-consumer or post-industrial sources.
- Specialized Materials:
- Depending on the specific requirements of the products being shipped, corrugated boxes may be manufactured using specialized materials. For example, boxes for temperature-sensitive pharmaceuticals might include insulating materials.
Understanding the materials used in corrugated shipper boxes is essential for assessing their suitability for different products, transportation conditions, and environmental considerations. Manufacturers often strive to balance strength and sustainability in the materials they choose
Strength and Durability
Strength and durability are critical characteristics of corrugated shipper boxes, making them a preferred choice for packaging and transporting goods. These qualities are a result of the materials used, the construction of the boxes, and their ability to withstand various external factors. Let’s delve into the factors contributing to the strength and durability of corrugated boxes:
- Material Selection:
Corrugated Medium: The corrugated medium, typically made of paperboard, adds strength and rigidity to the box. Its fluted structure enhances the overall durability of the packaging.
Liners: The outer layers, or liners, provide additional strength and a smooth surface. They are usually made from paperboard, contributing to the box’s structural integrity.
- Corrugated Structure:
The corrugated structure itself is a key factor in the strength of the box. The combination of the fluted medium and liners creates a resilient and supportive framework.
- Construction Techniques:
The process of folding and gluing the corrugated medium between the liners is carefully executed during manufacturing. Proper construction techniques are essential for creating a robust and durable box.
- Layer Configurations:
Single-wall, double-wall, and triple-wall configurations are available. Adding more layers increases the strength and weight-bearing capacity of the box, allowing it to accommodate heavier or more delicate items.
- Edge Crush Test (ECT):
ECT is a standard method for evaluating the compression strength of corrugated boxes. It measures the force the box can withstand at its edges without collapsing. Higher ECT values indicate greater strength.
- Burst Strength:
Burst strength measures the ability of a box to withstand internal pressure. It is particularly relevant for products that may exert pressure from within the packaging. High burst strength is essential for preventing box failure.
- Tape and Adhesive Quality:
The adhesive used to bond the layers of the box must be strong and resilient. Additionally, the quality of the tape used for sealing is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the packaging during transit.
- Customization for Specific Products:
Corrugated boxes can be customized based on the specific requirements of the products they will contain. Customization may include adding extra layers, partitions, or inserts for increased protection.
- Environmental Resistance:
Corrugated boxes can be treated with coatings to enhance resistance to environmental factors, such as moisture. This is important for protecting the contents from damage during transportation and storage.
- Testing and Quality Control:
Stringent testing and quality control measures during the manufacturing process ensure that corrugated boxes meet industry standards. This includes monitoring factors like material thickness, adhesive strength, and overall box performance.
In conclusion, the strength and durability of corrugated shipper boxes result from a combination of thoughtful design, quality materials, and manufacturing processes. These features make corrugated boxes reliable for safely transporting and protecting a wide range of products in various industries.
Kinds of corrugated shipper boxes
Corrugated shipper boxes come in various types, each designed for specific purposes and industries. Here are some common kinds of corrugated shipper boxes:
- Regular Slotted Container (RSC):
This is the most common type of corrugated box. It has four flaps on the top and bottom that meet in the center when closed. RSC boxes are widely used for shipping and storage.
- Full Overlap Container (FOL):
FOL boxes have flaps that fully overlap on the top and bottom. They offer extra stacking strength and protection, making them suitable for heavier or fragile items.
- Half-Slotted Container (HSC):
HSC boxes are similar to RSC but have only one set of flaps. They are often used as lids for other boxes or when an open-top design is required.
- One-Piece Folders (OPF):
OPF boxes are typically used for flat or narrow products. They consist of a single piece with flaps that fold to create the box. They are easy to assemble and are suitable for items like books or printed materials.
- Telescoping Boxes:
Telescoping boxes consist of two parts – a larger outer box and a smaller inner box that slides into the larger one. This design is often used for sets of products or items that need extra protection.
- Die-Cut Boxes:
Die-cut boxes are custom-shaped boxes that are cut and scored to create unique designs. They are often used for specialized or high-end products
- Five-Panel Wrap:
These boxes are formed by a single piece with five scored panels. They are suitable for products with irregular shapes or dimensions.
- Gaylord Boxes:
Gaylord boxes are large, bulk containers typically used for shipping and storing large quantities of items. They are commonly used in industries like agriculture, manufacturing, and retail.
- Double Cover Box:
This type of box has two separate covers, making it easy to access the contents without fully opening the box. It’s useful for products that may need frequent access or inspection.
- Trays and Lids:
Trays and lids are two-piece boxes where the tray serves as the base, and the lid fits over the top. They are commonly used for retail packaging and display purposes.
- Self-Erecting Boxes:
These boxes are pre-glued and can be easily assembled without the need for tape or staples. They are convenient for quick packing in manufacturing or fulfillment settings.
- Heavy-Duty Boxes:
Heavy-duty corrugated boxes are designed to withstand heavier loads and provide extra protection. They are suitable for industrial and heavy manufacturing applications.
These are just a few examples, and there are numerous other variations based on specific industry requirements and product characteristics. The choice of corrugated box type depends on factors such as the size and weight of the product, the mode of transportation, and the desired level of protection.
The corrugated structure
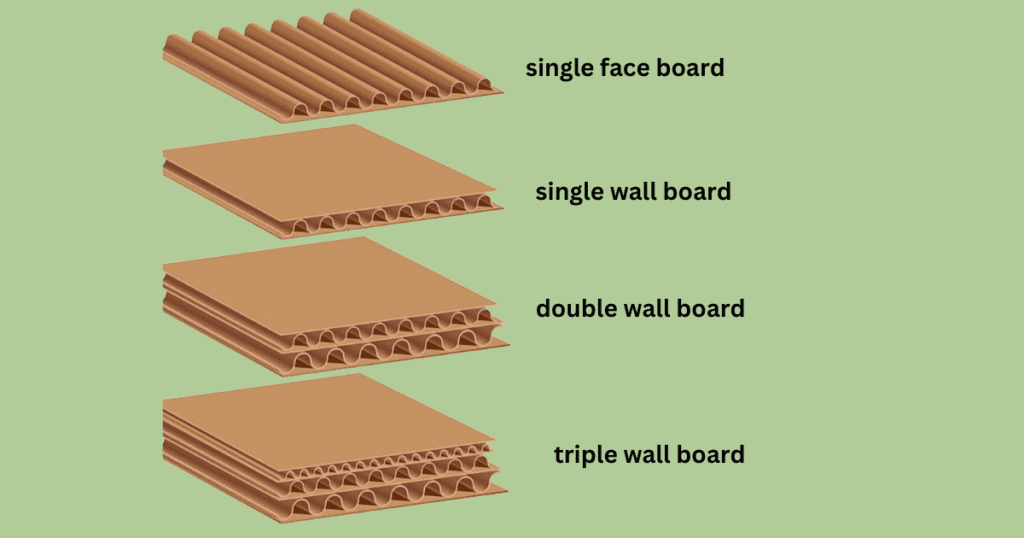
In the context of corrugated boxes, the terms “flute type” and “wall type” refer to specific characteristics of the corrugated structure. Corrugated boxes are made from a combination of liners and corrugated medium, and the flute type and wall type play a crucial role in determining the strength, rigidity, and protective qualities of the box. Let’s explore these terms:
Flute Type:
The flute is the wavy inner layer of corrugated cardboard that provides strength and support to the box. There are several types of flutes, and the choice of flute type depends on the specific requirements of the packaging.
Common flute types include:
- A-Flute: This is the original flute type and provides the highest level of stiffness and cushioning. It is often used for packaging fragile items.
- B-Flute: Smaller and denser than the A-flute, the B-flute offers good stacking strength and crushing resistance. It is commonly used for shipping boxes.
- C-Flute: This type is the most commonly used flute. It provides a balance between A and B flutes, offering good stacking strength and crush resistance. C-flute is versatile and is used in various packaging applications.
- E-Flute: E-flute is a thin flute type with a greater number of flutes per linear foot compared to larger flutes like A, B, or C. It provides a smooth surface, making it suitable for high-quality printing. Offers good crush resistance but may not have the stacking strength of larger flutes. Takes up less space, making it an excellent choice for retail packaging and displays. They are often used for packaging products like cosmetics, small electronics, and other lightweight items.
- F-Flute: The f-flute is even thinner than the E-flute, making it one of the smallest flute types. Extremely fine flute structure with a higher number of flutes per linear foot. It provides a flat surface, making it ideal for high-quality printing. Offers excellent printability and die-cutting capabilities. Used for packaging applications where a thin profile and a high level of detail in printing are essential. Suitable for products like small consumer goods, food items, and other lightweight items
Wall Type:
The wall type refers to the combination of corrugated layers and liners in a corrugated box.
- Single Wall:
Description: A single wall consists of one layer of corrugated medium (flute) that is glued between two flat sheets of linerboard.
Characteristics:
- Lightweight and cost-effective.
- Suitable for a wide range of applications,
- Particularly when the contents are not excessively heavy or fragile.
- Provides basic protection and strength.
- Double Wall:
Description: The double wall consists of two layers of corrugated medium separated by three flat sheets of linerboard (one on each outer side and one between the two corrugated layers).
Characteristics:
- Offers greater strength and durability compared to a single wall.
- Provides enhanced protection, making it suitable for heavier or more delicate items.
- Better stacking strength and crush resistance.
- Triple Wall:
Description: The triple wall consists of three layers of corrugated medium separated by four flat sheets of linerboard.
Characteristics:
- The most robust option among the three.
- Designed for heavy-duty applications and extremely high stacking strength.
Used for shipping large and heavy items or for applications where maximum protection is required.
The choice between single wall, double wall, and triple wall depends on the specific packaging requirements, such as the weight and fragility of the product, the shipping conditions, and the desired level of protection. Single walls are often suitable for everyday packaging needs, while double walls and triple walls